Computers and Networks (Unit 4)
Add Definitions from Unit 4 Computer Systems and Networks
Requirements
Work through College Board Unit 4… blog, add definitions, and pictures. Be creative, for instance make a story of Computing and Networks that is related to your PBL experiences this year.
How a Computer Works
As we have learned, a computer needs aa program to do something smart. The sequence of a program initiates a series of actions with the computers Central Processing Unit (CPU). This component is essentially a binary machine focussing on program instructions provided. The CPU retrieives and stores the data it acts upon in Random Access Memory (RAM). Between the CPU, RAM, and Storage Devices a computer can work with many programs and large amounts of data.
List specification of your Computer, or Computers if working as Pair/Trio
- Processor GHz: 1.4
- Memory in GB: 4, 1600 MHz DDR3
- Storage in GB: 128
- OS: macOS Big Sur
Define or describe usage of Computer using Computer Programs. Pictures are preferred over a lot of text. Use your experience.
- Input Devices: These are devices that allow users to input data or commands into a computer. Examples include a keyboard, mouse, microphone, and scanner.
- Output Devices: These are devices that allow a computer to communicate information back to the user. Examples include a monitor, printer, and speakers.
- Program File: A program file is a file that contains instructions for a computer program to execute. Examples include an executable file (.exe), a script file (.sh), and a batch file (.bat).
- Program Code: Program code is a set of instructions written in a programming language that tells a computer what to do.
- Processes: A process is a program that is currently running on a computer.
- Ports: A port is a physical interface on a computer that allows it to connect to other devices. Examples include USB ports, HDMI ports, and Ethernet ports. Ports
- Data File: A data file is a file that contains information that can be used by a computer program. Examples include a text file (.txt), a spreadsheet file (.xls), and an image file (.jpg).
- Inspect Running Code: Inspecting running code allows programmers to monitor the behavior of their programs as they run.
- Inspect Variables: Inspecting variables allows programmers to view the current values of variables in their programs.

The Internet
Watch/review College Board Daily Video for 4.1.1
- Essential Knowledge
- A computing device is a physical artifact that can run a program. Some examples include computers, tablets, servers, routers, and smart sensors.
- A computing system is a group of computing devices and programs working together for a common purpose.
- A computer network is a group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data.
- A computer network is a type of computing system.
- A path between two computing devices on a computer network (a sender and a receiver) is a sequence of directly connected computing devices that begins at the sender and ends at the receiver.
- Routing is the process of finding a path from sender to receiver.
- The bandwidth of a computer network is the maximum amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time.
- Bandwidth is usually measured in bits per second
-
Complete Vocabulary Matching Activity. Incorporate this into your learnings from year. To analyze measure path and latency use
tracerouteandpingcommands from Linux Terminal. - Path: A (sequence of computing devices that sends information between each other)
- Route: E (finding a path between multiple servers)
- Computer System: B (group of computing devices working together)
- Computer Device: C (physical device to run programs using cpu/memory/etc)
- Bandwidth: D (max amt of data that can be sent over the network)
-
Computer Network: F (interconnected computers that send and recieve data amongst each other)
- Path - A sequence of directly connected computing devices that begins at the sender and ends at the receiver.
- Route - The process of finding a path from sender to receiver.
- Computer System - A group of computing devices and programs working together for a common purpose.
- Computer Device - A physical artifact that can run a program, such as a computer, tablet, or smart sensor.
- Bandwidth - The maximum amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time.
- Computer Network - A group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data.
- To analyze and measure path and latency, you can use the traceroute and ping commands from the Linux Terminal.
- traceroute - This command is used to trace the path that a packet takes from a sender to a receiver, showing the IP addresses of each device in the path. It can also provide information on the round-trip time (RTT) of packets to each device along the path.
- ping - This command is used to test the reachability of a device on a network and measure the latency of packets sent between devices. It sends packets to a specific IP address and measures the time it takes for a response to be received.
Watch/review College Board Daily Video 4.1.2
- Complete True of False Questions
T: Open standards and protocols enable different manufacturers and developers to build hardware and software that can communicate with hardware and software on the rest of the internet.
F: IETF is a task force used to enforce laws to keep manufacturers out of the internet.
F: Routes are determined in advance and are not flexible.
T: A protocol is an agreed-upon set of rules that specify the behavior of a system.
F: UDP guarantees transfers and is faster.
F: The World Wide Web is the internet.
T: HTTP is a protocol used by the World Wide Web.
- Essential Knowledge
- The internet is a computer network consisting of interconnected networks that use standardized, open (nonproprierary) communication protocols.
- Access to the internet depends on the ability to connect a computing device to an internet connected device.
- A protocol is an agreed-upon set of rules that specify the behavior of a system.
- The protocols used in the internet are open, which allows users to easily connect additional computing devices to the internet.
- Routing on the internet is usually dynamic; it is not specified in advance
- The scalability of a system is the capacity for the system to change in size and scale to meet new demands.
- The internet was designed to be scalable
- Information is passed through the internet as a data stream. Data streams contain chunks of data, which are encapsulated in packets.
- Packets contain a chunk of data and metadata used for routing the packet between the origin and the destination on the internet, as well as for data reassembly.
- Packets may arrive at the destination in order, out of order, or not at all
- IP, TCP and UDP are common protocols used on the internet.
- The world wide web is a system of linked pages, programs, and files.
- HTTP is a protocol used by the world wide web
- The world wide web uses the internet
- Go over AP videos, vocabulary, and essential knowledge. Draw a diagram showing the internet and its many levels. A preferred diagram would using your knowledge of frontend, backend, deployment, etc. Picture would highlight vocabulary by illustration. The below illustration have some ideas
Created:
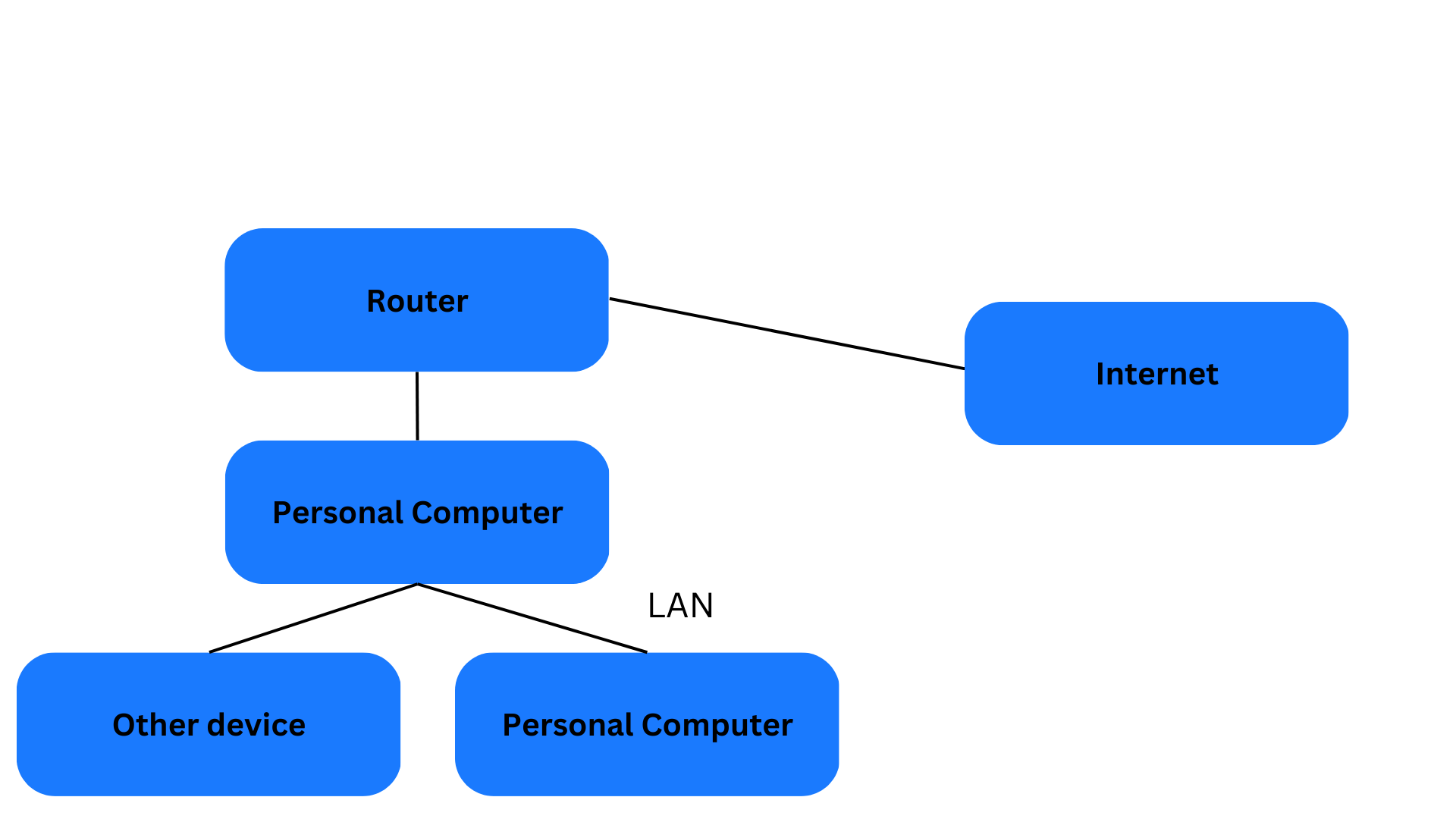
Online image I found:
Personal computer --> Send and receive a packet over a network, which make up parts of file
Work on computer systems
Computer network which are connected and can transfer data
Use a path which the message takes
Router helps route along the path
Bandwidth refers to the speed at which packages can flow
Protocols help make rules for a system
IP - sets packets with metadata and is put on path through router indicates direction or location of computer
DNS - gives domains to IP, maps names to IPS
World Wide Web - linked data pages
HTTP - links to web servers, usually port 80
HTTPS - HTTP with security, usually port 4443
TCP - ensures that the packet has been transmitted
UDP - tries best to deliver packet
HTTP -
Network Access allows us to get on to the network
LAN - Physical connections to a network, connection to the same network
Hop on to autonomous system controlled by internet providers
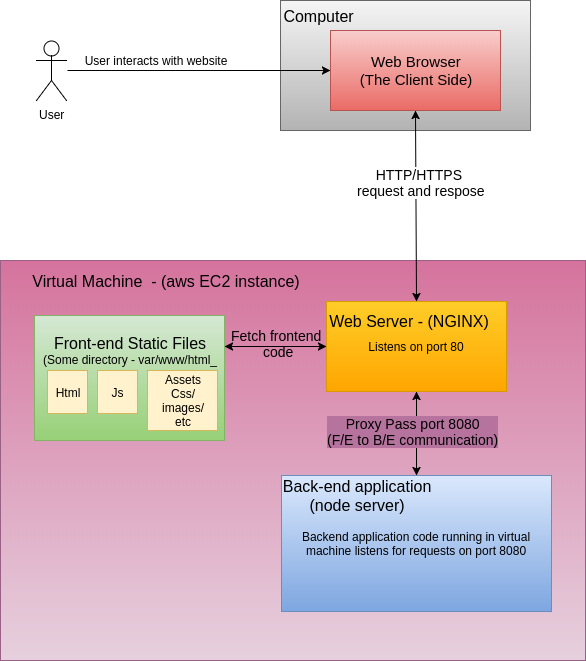
- Often we draw pictures of machines communicating over the Internet with arrows. However, the real communication goes through protocol layers and the machine and then is trasported of the network. For College Board and future Computer Knowledge you should become familiar with the following …
User Machine <---> Frontend Server <---> Backend Server
+-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+
| Browser | | GH Page | | Flask |
+-----------+ ^ +-----------+ ^ +-----------+
| HTTP | | | HTTP | | | HTTP |
+-----------+ | +-----------+ | +-----------+
| TCP | | | TCP | | | TCP |
+-----------+ | +-----------+ | +-----------+
| IP | V | IP | V | IP |
+-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+
| Network | <---> | Network | <---> | Network |
+-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+
The “http” layer is an application layer protocol in the TCP/IP stack, used for communication between web browsers and web servers. It is the protocol used for transmitting data over the World Wide Web.
The “transport” layer (TCP) is responsible for providing reliable data transfer between applications running on different hosts. The TCP protocol segments the data into smaller chunks called “segments”. Each segment contains a sequence number that identifies its position in the original stream of data, as well as other control information such as source and destination port numbers, and checksums for error detection.
The “ip” layer is responsible for packetizing data received from the TCP layer of the protocol stack, and then encapsulating the data into IP packets. The IP packets are then sent to the lower layers of the protocol stack for transmission over the network.
The “network” layer is responsible for routing data packets between networks using the Internet Protocol (IP). This layer handles tasks such as packet addressing and routing, fragmentation and reassembly, and network congestion control.
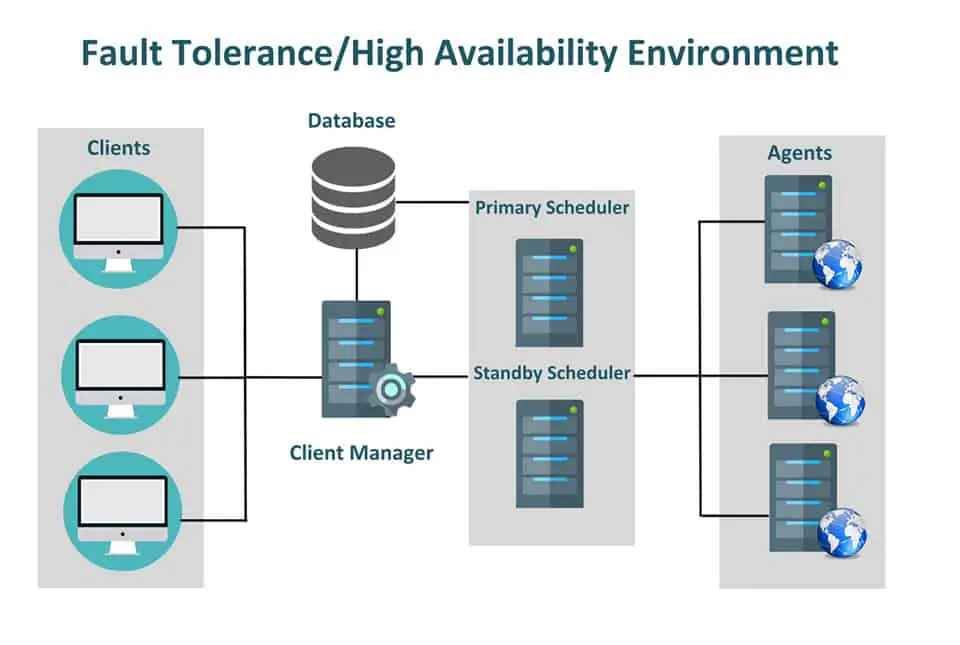
Fault Tolerance
Watch both Daily videos for 4.2
- Complete the network activity, summarize your understanding of fault tolerance.
Fault tolerance allows us to be able to continue computer tasks even if there are problems with hardware or software. Fault tolerance helps provide alternate paths for devices in order to be able to ensure tasks will be completed. To be fault tolerant, paths will need to be redundant and use more resources, but in order to ensure the network can work in light of failures. More devices can create a stronger network.
Parallel and Distributed Computing
Review previous lecture on Parallel Computing and watch Daily vidoe 4.3. Think of ways to make something in you team project to utilize Cores more effectively. Here are some thoughts to add to your story of Computers and Networks…
- What is naturally Distributed in Frontend/Backend archeticture?
The frontend is what environment is displayed to the user. The backend is the data which is stored in the backend layer. The frontend is responsible for the user interface and appearing presentable, while the backend is responsible for data storage. Dividing them into two components allows us to have more efficient systems.
- Analyze this command in Docker:
ENV GUNICORN_CMD_ARGS="--workers=1 --bind=0.0.0.0:8086". Determine if there is options are options in this command for parallel computing within the server that runs python/gunicorn. Here is an article
The environment variable is named ENV GUNICORN_CMD_ARGS with two things specified. The –workers=1 specifies to not have parallel computing, since there is one worker. –bind=0.0.0.0:8086 establishes the port and address to bind to.
Last week we discussed parallel computing on local machine. There are many options. Here is something to get parallel computing work with a tool called Ray.
- Review this article… Can you get parallel code on images to work more effectively? I have not tried Ray.
- Code example from ChatGPT using squares. This might be more interesting if nums we generated to be a lot bigger.
import ray
# define a simple function that takes a number and returns its square
def square(x):
return x * x
# initialize Ray
ray.init()
# create a remote function that squares a list of numbers in parallel
@ray.remote
def square_list(nums):
return [square(num) for num in nums]
# define a list of numbers to square
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# split the list into two parts
split_idx = len(nums) // 2
part1, part2 = nums[:split_idx], nums[split_idx:]
# call the remote function in parallel on the two parts
part1_result = square_list.remote(part1)
part2_result = square_list.remote(part2)
# get the results and combine them
result = ray.get(part1_result) + ray.get(part2_result)
# print the result
print(result)